Introduction
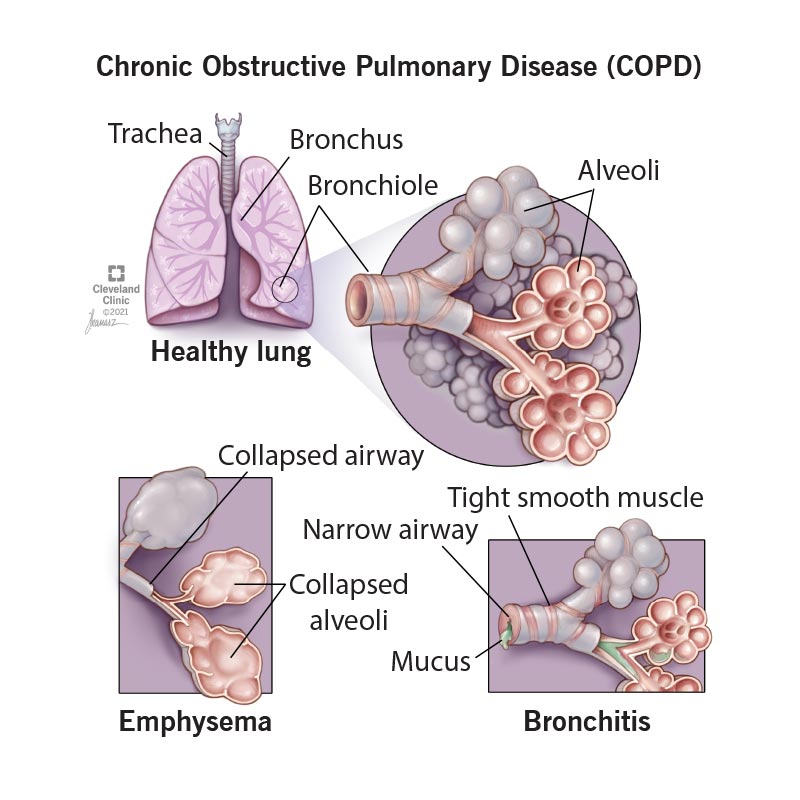
Creating a nursing care plan for a patient with chronic bronchitis involves addressing respiratory symptoms, promoting airway clearance, and managing potential complications. Below is a sample nursing care plan:
-
Assessment:
Subjective Data:
- Obtain a detailed medical history, including the duration and severity of chronic bronchitis, previous exacerbations, and current medications.
- Interview the patient to assess symptoms such as cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and fatigue.
Objective Data:
- Monitor respiratory rate, pattern, and effort.
- Auscultate lung sounds for signs of wheezing, crackles, or diminished breath sounds.
- Assess oxygen saturation levels.
-
Nursing Diagnosis:
Ineffective Airway Clearance related to excessive mucus production and bronchoconstriction in chronic bronchitis.
Goals:
- The patient will achieve improved airway clearance.
- The patient will demonstrate effective coughing and expectoration techniques.
Interventions:
Encourage and assist with effective coughing techniques, such as deep breathing followed by controlled coughing. Administer prescribed bronchodilators and mucolytic medications as directed. Encourage increased fluid intake to promote thinning of respiratory secretions. Collaborate with respiratory therapy to perform chest physiotherapy and postural drainage. Monitor and document sputum characteristics and respiratory status.
-
Nursing Diagnosis:
Impaired Gas Exchange related to airflow limitation and decreased oxygen saturation in chronic bronchitis.
Goals:
- The patient will achieve improved gas exchange.
- The patient will maintain adequate oxygenation.
Interventions:
Administer prescribed bronchodilators and corticosteroids as directed. Monitor oxygen saturation levels and administer supplemental oxygen as prescribed. Encourage and assist with pursed-lip breathing to promote prolonged exhalation. Elevate the head of the bed to facilitate optimal lung expansion. Collaborate with the healthcare team to assess the need for pulmonary rehabilitation.
-
Nursing Diagnosis:
Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to bronchoconstriction and increased respiratory effort.
Goals:
- The patient will achieve effective breathing patterns.
- The patient will report relief from respiratory distress.
Interventions:
Administer prescribed bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications as directed. Monitor respiratory rate, depth, and effort regularly. Encourage and assist with activities that promote optimal lung expansion, such as turning and deep breathing. Implement relaxation techniques and breathing exercises. Collaborate with the healthcare team to consider alternative pain management strategies, such as breathing exercises or relaxation techniques.
-
Nursing Diagnosis:
Fatigue related to increased work of breathing and chronic inflammation in chronic bronchitis.
Goals:
- The patient will report decreased fatigue.
- The patient will demonstrate energy conservation techniques.
Interventions:
Schedule rest periods between activities to prevent exhaustion. Teach energy conservation techniques, such as pacing activities and prioritizing tasks. Encourage and assist with activities of daily living to minimize exertion. Collaborate with the patient to establish realistic goals and expectations. Monitor the patient’s response to interventions and adjust the care plan accordingly.
-
Evaluation:
- Regularly assess the patient’s progress toward established goals.
- Modify the care plan based on changes in the patient’s condition or needs.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to ensure comprehensive and patient-centered care.
Note: The nursing care plan should be individualized based on the patient’s specific needs, preferences, and healthcare provider’s recommendations. Regular communication with the patient and healthcare team is essential for the effective management of chronic bronchitis.